Introduction:
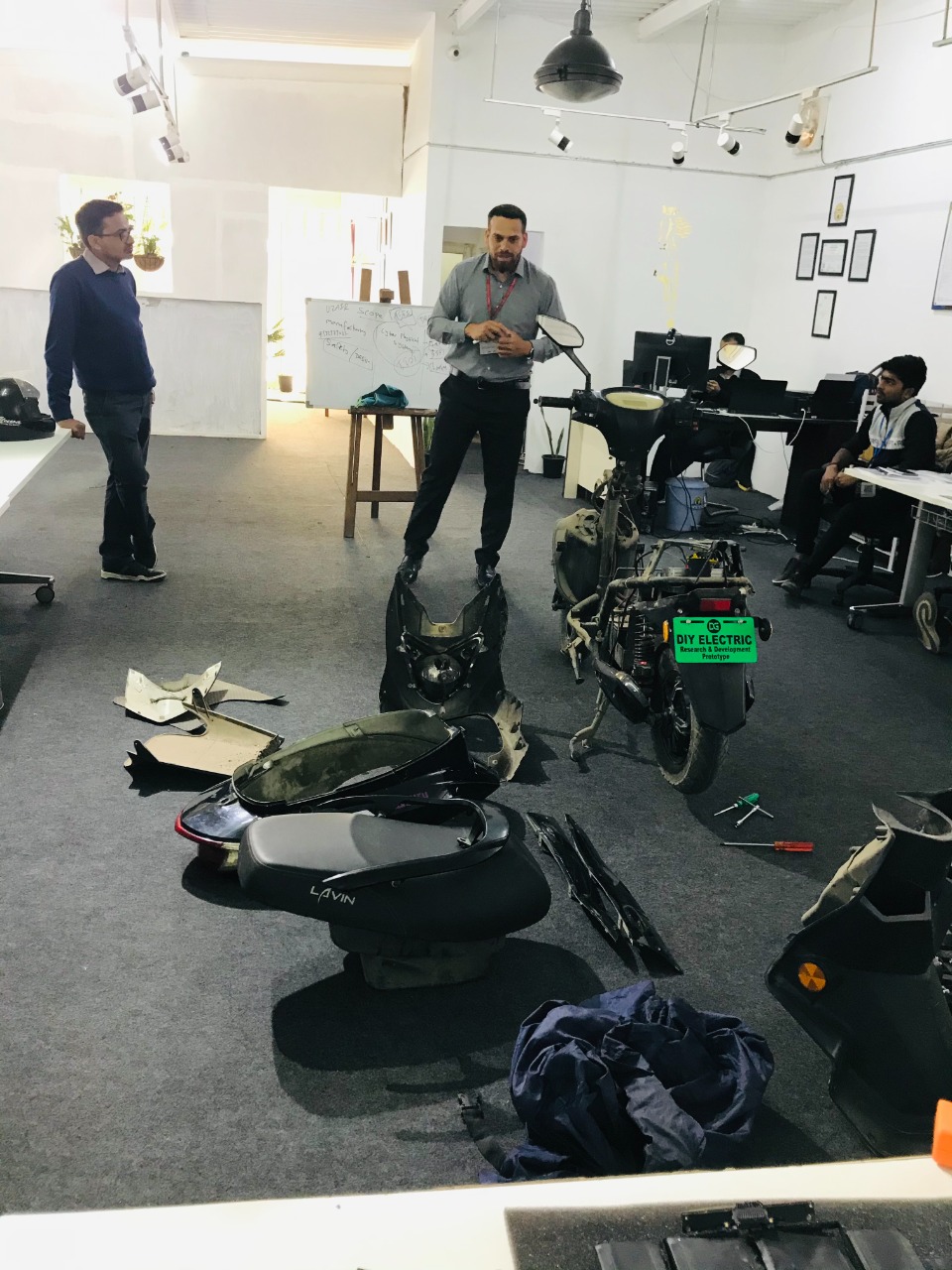
Retrofitting traditional vehicles to electric vehicles (EVs) is becoming increasingly popular due to the environmental benefits and cost savings that EVs offer. However, to ensure the safety and reliability of retrofitted EVs, they must undergo testing and homologation. In this blog post, we will discuss the testing and homologation rules for electric vehicle retrofitting.
What is Electric Vehicle Retrofitting?
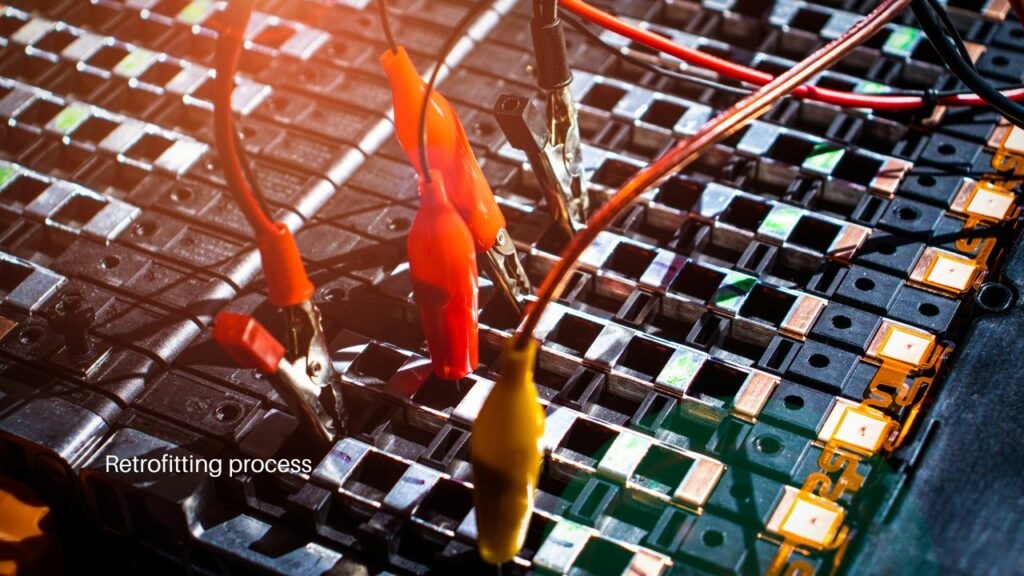

Electric vehicle retrofitting is the process of converting a traditional vehicle into an electric vehicle. The process involves installing an electric motor, battery, and other components necessary for an electric vehicle to function.
Need for Testing and Homologation:
Testing and homologation are necessary to ensure the safety and reliability of retrofitted electric vehicles. Retrofitted EVs must meet the same safety and performance standards as factory-built EVs.
Testing and Homologation Process for Electric Vehicle Retrofitting:
The testing and homologation process for electric vehicle retrofitting can be broken down into the following steps:
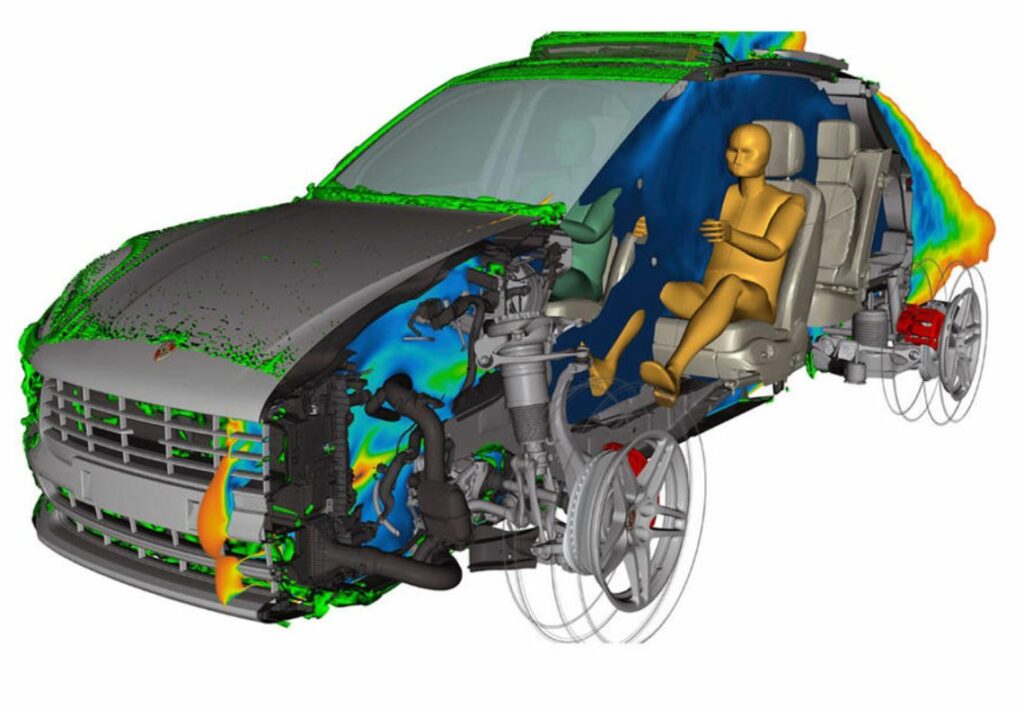
a. Electrical Safety Testing:
Electrical safety testing involves testing the electrical components of the retrofitted EV to ensure that they meet safety standards. This includes testing for electrical insulation, protection against electric shock, and protection against overcurrent.
b. Electromagnetic Compatibility Testing:
Electromagnetic compatibility testing involves testing the retrofitted EV for electromagnetic interference (EMI) and electromagnetic susceptibility (EMS). This is important to ensure that the retrofitted EV does not interfere with other electronic devices or systems and that it is not affected by external electromagnetic fields.
c. Mechanical Safety Testing:
Mechanical safety testing involves testing the retrofitted EV for mechanical safety. This includes testing for structural integrity, crashworthiness, and occupant protection.
d. Performance Testing:
Performance testing involves testing the retrofitted EV for performance parameters such as range, acceleration, and top speed. This is important to ensure that the retrofitted EV meets the performance standards of a factory-built EV.
e. Certification and Homologation:
Once the retrofitted EV has passed all the necessary tests, it must be certified and homologated by the appropriate regulatory body. This certification and homologation process ensures that the retrofitted EV meets all regulatory requirements for safety and performance.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, testing and homologation are necessary to ensure the safety and reliability of retrofitted electric vehicles. The testing and homologation process for electric vehicle retrofitting involves testing for electrical safety, electromagnetic compatibility, mechanical safety, and performance. Retrofitted electric vehicles must meet the same safety and performance standards as factory-built electric vehicles to ensure their safety and reliability on the road. It is important for anyone considering retrofitting a vehicle to electric to understand the testing and homologation process and ensure that their retrofitted EV meets all necessary safety and performance standards.
FAQs
Q.1 What is electric vehicle retrofitting?
Ans. Electric vehicle retrofitting is the process of converting a traditional vehicle into an electric vehicle by installing an electric motor, battery, and other necessary components.
Q.2 Why is testing and homologation important for electric vehicle retrofitting?
Ans. Testing and homologation are important for electric vehicle retrofitting to ensure the safety and reliability of the retrofitted electric vehicle. Retrofitted EVs must meet the same safety and performance standards as factory-built EVs.
Q.3 What is electrical safety testing?
Ans. Electrical safety testing involves testing the electrical components of the retrofitted EV to ensure that they meet safety standards. This includes testing for electrical insulation, protection against electric shock, and protection against overcurrent.
Q.4 What is electromagnetic compatibility testing?
Ans. Electromagnetic compatibility testing involves testing the retrofitted EV for electromagnetic interference (EMI) and electromagnetic susceptibility (EMS) to ensure that it does not interfere with other electronic devices or systems and that it is not affected by external electromagnetic fields.
Q.5 What is mechanical safety testing?
Ans. Mechanical safety testing involves testing the retrofitted EV for mechanical safety, including testing for structural integrity, crashworthiness, and occupant protection.
Q.6 What is performance testing?
Ans. Performance testing involves testing the retrofitted EV for performance parameters such as range, acceleration, and top speed to ensure that it meets the performance standards of a factory-built EV.
Q.7 Who is responsible for testing and homologation of retrofitted electric vehicles?
Ans. The regulatory body responsible for testing and homologation of retrofitted electric vehicles varies by country or region.
Q.8 What are the consequences of not getting a retrofitted electric vehicle homologated?
Ans. A retrofitted electric vehicle that has not been homologated may not be legal to drive on public roads, and the owner may face fines or other penalties.
Q.9 How long does the testing and homologation process take?
Ans. The testing and homologation process for retrofitted electric vehicles can vary in time depending on the complexity of the retrofit and the regulatory body responsible for homologation.
Q.10 Can a retrofitted electric vehicle be sold or transferred to another owner after homologation?
Ans. Yes, a retrofitted electric vehicle that has been homologated can be sold or transferred to another owner as long as it meets the necessary safety and performance standards. The new owner will need to ensure that the vehicle is still in compliance with regulations in their respective region.























