“EV” is a common shorthand for “electric vehicle.” Electric Vehicle is defined as a mobility machine through which electricity runs via an electric motor to move – or help move – the car. However, it solely doesn’t refer to as all the electronic vehicles but when an individual is saying EV, he/she basically means BEV (Battery Electric Vehicle). The term EV consists of BEV’s, PHEV’s (Plugin Hybrid Electric Vehicle), PIV’s (Plug-in vehicle) ,ULEV’s (ultra low emissions vehicle) and REX’s (Range Extender type of PHEV).
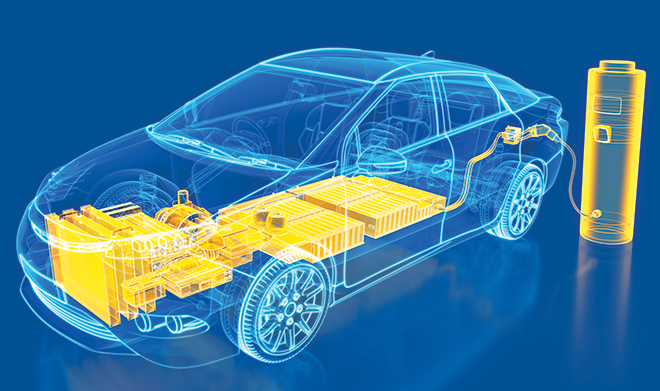
An electric vehicle (EV) is a type of vehicle that runs on electricity. Electric automobiles and trucks use an electric motor that is powered by electricity from batteries or a fuel cell instead of the typical engines that are driven by gasoline (petrol) or diesel. Having zero exhaust emissions gives EVs a considerable advantage over traditional modes of transportation in terms of the ability to reduce pollution.
How does an electric car function?
EVs lack an internal combustion engine in favour of an electric motor (ICE). The engine of the vehicle is powered by a sizable traction battery pack, which needs to be charged at a charging station or wall outlet. The majority of electric vehicles (EVs) use lithium-ion batteries, which outperform most other viable batteries in terms of energy density, lifespan, and power.
EVs come in three basic categories. Both plug-in hybrid EVs and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) run on both gasoline and electricity. While the latter can recharge using any external source of electricity, the former creates energy through the car’s own braking system. Battery EVs (BEVs), on the other hand, are completely electric, meaning that they produce no emissions.

















