As the name suggests, an automatic night lamp can automatically turn the light on and off without the need for human intervention. It determines whether it is day or night by sensing the surroundings’ light intensity. Additionally, it automatically turns ON when it detects darkness and OFF when it detects light. A sensor called LDR is utilized to distinguish the light force. This task finds wide outside applications in roads, nurseries and public spots where it tracks down trouble to select an individual to work the lights.
Components Required
- Light Dependent Resistor (LDR)
- LM358 Op-Amp
- Resistor 22KΩ
- Resistor 10KΩ
- Preset 10KΩ
- BC547 transistor
- 1N4148 diode
Circuit Diagram
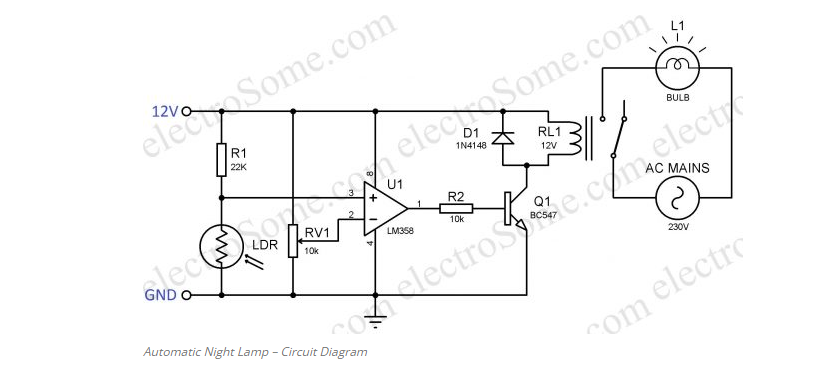
Working
The light dependent resistor, or LDR, is the circuit’s most important component. A particular kind of resistor known as a sensor has a resistance that decreases when it is exposed to light. In the dark, it also has a high resistance. From a few hundred ohms to the mega ohm range, the resistance value changes. A potential divider network houses the LDR. Therefore, light intensity influences voltage across the LDR. The positive terminal of a comparator receives voltage from the LDR. Now, to compare the voltage across LDR with a reference voltage, The pot or preset is used to determine that reference voltage. As a result, the circuit’s sensitivity can be modified with this preset. The comparator, which is made with an LM358 op-amp, compares the voltage levels at its two inputs and produces an appropriate output. The output will be high if the voltage at the positive terminal is higher, while the voltage at the negative terminal will be lower. That is, if it is dark, the voltage at the positive terminal will be higher than the reference voltage due to the high resistance across the LDR. As a result, the comparator’s output will be high. The result of comparator is given to a semiconductor wired as a switch. The transistor conducts and current flows through the relay coils when there is sufficient voltage across the base-emitter junction. As a result, the bulb turns on as the relay switches its contact. Since the bulb should be off when the relay coils are not energized, it is connected to the relay’s NO (Normally Open) pin. In the event that the result of comparator is low, semiconductor will be in OFF stage. So no ongoing courses through the hand-off and bulb stays in OFF stage.
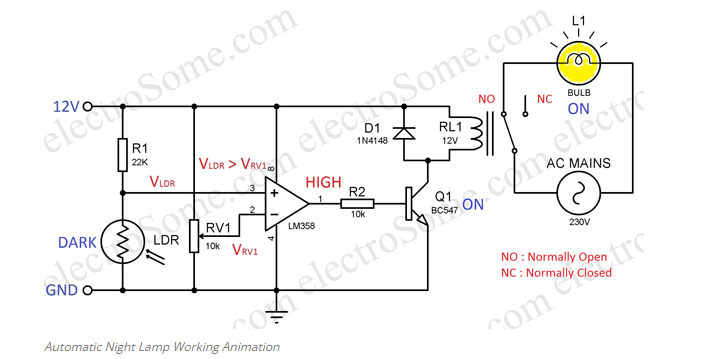
You can choose a voltage between 3 to 32V for powering this circuit depending of the relay coil voltage. I choose 12V since 12V relays are very common in the market.
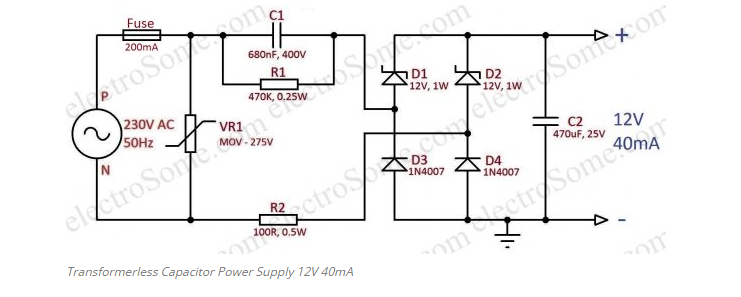
Power Supply
A power supply with a capacitor dropper is my choice. I used the 12V, 40mA supply in the following circuit to accomplish that. For more information, please refer to the article, Transformerless Capacitor Power Supply.
- 12V Relay

















