A microchip comprises a strong central processor on a solitary chip while interfacing with an outer fringe; the microcontroller puts a computer chip and peripherals on a solitary chip.

Let’s talk about the differences between microprocessors and microcontrollers, as well as their definitions, types, and functions.
Table of Contents
- What is a microprocessor?
- Types of microprocessors
- What is microcontroller?
- Types of microcontrollers
- Difference between microprocessor and microcontroller
What is a Microprocessor?
A microprocessor is a controlling unit of a micro-computer wrapped inside a small chip. It performs Arithmetic Logical Unit (ALU) operations and communicates with the other devices connected with it. It is a single Integrated Circuit in which several functions are combined.
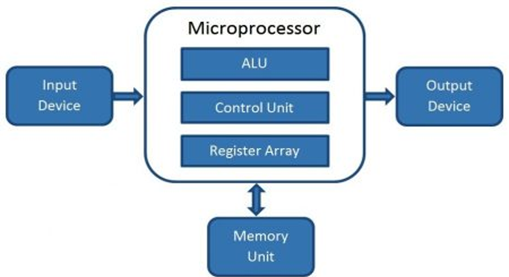
What are the types of Microprocessor?
Important types of Microprocessors are:
- Complex Instruction Set Microprocessors
- The Application Specific Integrated Circuit
- Reduced Instruction Set Microprocessors
- Digital Signal Multiprocessors (DSPs)
What is Microcontroller?
A chip that is made to control electronic devices is called a microcontroller. It is stored in a single integrated circuit that is designed to carry out a specific function and run a particular application.
It is frequently utilized in electronic devices that are automatically controlled and are designed specifically for embedded applications. It contains memory, processor, and programmable I/O.
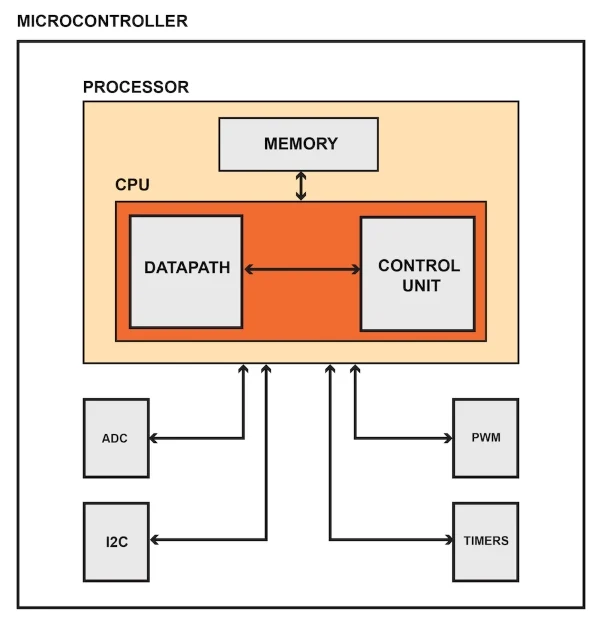
What are the types of Microcontroller?
Here are important types of Microcontroller:
- 8 bit Microcontroller
- 16 bit Microcontroller
- 32 bit Microcontroller
- Embedded Microcontroller
- External memory Microcontroller
History of Microprocessor
Here, are the important landmark from the history of Microprocessor
- Fairchild Semiconductors invented the first IC (Integrated Circuit) in 1959.
- In 1968, Robert Noyce, Gordan Moore, Andrew Grove found their own company Intel.
- Intel grew from 3 man start-up in 1968 to industrial giant by 1981.
- In 1971, INTEL created the first generation Microprocessor 4004 that would run at a clock speed of 108 kHz
- From 1973 to 1978, second-generation 8-bit microprocessors were fabricated like Motorola 6800 and 6801, INTEL-8085, and Zilog’s-Z80.
- In 1978, Intel 8008 third-generation process came into the market.
- In the early 80s, Intel released fourth-generation 32-bit processors.
- In 1995, intel released in fifth-generation 64-bit processors .
History of Microcontroller
Here, are important landmarks from the history of Microcontroller:
- First used in 1975(Intel 8048)
- The introduction of EEPROM in 1993
- The same year, Atmel introduced the first microcontroller using Flash memory.
Difference between Microprocessor and Microcontroller:
Here is the difference between Microprocessor vs. Microcontroller
| Microprocessor | Microcontroller |
|---|---|
| Microprocessor is the heart of Computer system. | Micro Controller is the heart of an embedded system. |
| It is only a processor, so memory and I/O components need to be connected externally | Micro Controller has a processor along with internal memory and I/O components. |
| Memory and I/O has to be connected externally, so the circuit becomes large. | Memory and I/O are already present, and the internal circuit is small. |
| You can’t use it in compact systems | You can use it in compact systems. |
| Cost of the entire system is high | Cost of the entire system is low |
| Due to external components, the total power consumption is high. Therefore, it is not ideal for the devices running on stored power like batteries. | As external components are low, total power consumption is less. So it can be used with devices running on stored power like batteries. |
| Most of the microprocessors do not have power saving features. | Most of the microcontrollers offer power-saving mode. |
| It is mainly used in personal computers. | It is used mainly in a washing machine, MP3 players, and embedded systems. |
| Microprocessor has a smaller number of registers, so more operations are memory-based. | Microcontroller has more register. Hence the programs are easier to write. |
| Microprocessors are based on Von Neumann model | Micro controllers are based on Harvard architecture |
| It is a central processing unit on a single silicon-based integrated chip. | It is a byproduct of the development of microprocessors with a CPU along with other peripherals. |
| It has no RAM, ROM, Input-Output units, timers, and other peripherals on the chip. | It has a CPU along with RAM, ROM, and other peripherals embedded on a single chip. |
| It uses an external bus to interface to RAM, ROM, and other peripherals. | It uses an internal controlling bus. |
| Microprocessor-based systems can run at a very high speed because of the technology involved. | Microcontroller based systems run up to 200MHz or more depending on the architecture. |
| It’s used for general purpose applications that allow you to handle loads of data. | It’s used for application-specific systems. |
| It’s complex and expensive, with a large number of instructions to process. | It’s simple and inexpensive with less number of instructions to process. |
What is microcontroller in battery?
The MCU is the brain inside the BMS. An MCU captures all the data from the sensors through its peripherals and processes the data based on the configuration file of the battery pack to make appropriate decisions.
Which microcontroller is used in BMS?
MPC5775B and MPC5775E Microcontrollers for Battery Management Systems (BMS) and Inverter Applications.
What is the important role of microprocessor and microcontroller in Electric Vehicle?
Microprocessors and microcontrollers play important roles in the operation of electric vehicles (EVs).
A microprocessor is a central processing unit (CPU) that performs arithmetic and logic operations, and controls the operation of other electronic devices in the EV. The microprocessor is responsible for controlling the motor speed and torque, managing the battery charging and discharging, and regulating the power electronics. It can also process data from various sensors and communicate with other systems in the EV.
On the other hand, a microcontroller is a specialized computer chip that contains a CPU, memory, and input/output interfaces. It is designed to control specific functions in the EV, such as the operation of the electric power steering system, the regenerative braking system, and the heating and cooling systems.
The microcontroller is responsible for monitoring and controlling various parameters in the EV, such as the battery voltage, temperature, and state of charge, and adjusting the vehicle’s performance accordingly. It can also communicate with other electronic systems in the EV, such as the infotainment system and the battery management system.
What is the function of microcontroller and microprocessor?
Function of Microprocessor and Microcontroller;
While microprocessors are the controlling unit of a micro-computer that is wrapped within a small chip, microcontrollers are chips that are optimized to control electronic devices. The two differ in their size, functionality and architecture on which they are based.
What are the application of microcontroller in electrical engineering?
Microcontrollers are used in automatically controlled products and devices, such as automobile engine control systems, implantable medical devices, remote controls, office machines, appliances, power tools, toys and other embedded systems.
What are the examples of microcontroller and microprocessor?
some popular examples of Microprocessor and Microcontroller;
Some popular examples of the microprocessor are Intel core i7, AMD Athlon, Broadcom BCM2711 (Raspberry Pi) etc, and some example for microcontrollers are ATmega328 (Arduino UNO), STM32, PIC16F877A etc.