EVs need to be charged, just like a cell phone, to maintain sufficient power. Using equipment to charge an electric vehicle (EV), electricity is delivered to the vehicle’s battery. To charge an electric vehicle, a EV charging station uses the electrical grid. Electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE) is the technical term for electric vehicle charging stations.
A home charging station, a public charging station, or a workplace charging station are all options for EV drivers to choose from.
The term “residential EV charging” refers to using a Level 2 charger to charge an electric vehicle at home (more on EV charging levels below).
The fleet of electric vehicles, multifamily units, and workplace charging stations all qualify for commercial electric car charging. Customers and employees alike are welcome to make use of commercial electric vehicle charging stations. Public access to many commercial EV charging stations is also available.
What is the meaning of EV charging?
EV charging is the process of using EV charging equipment to deliver electricity to the car’s battery. An EV charging station taps into the electrical grid to charge an EV. The technical term for EV charging stations is electric vehicle supply equipment.
What is EV and how it works?
An electric vehicle uses a battery to store electrical energy that is ready to use. A battery pack is made up of a number of cells that are grouped into modules. Once the battery has sufficient energy stored, the vehicle is ready to use. Battery technology has improved hugely in recent years.
How is EV vehicles charged?
Yes, you can charge it at home. With Type 1 AC charger, you can charge from an AC socket, but at 3 kWh it is too slow. The Type 2 or wallbox charger is usually installed by car companies (for free currently) at home and is faster. Besides these, there are other faster chargers too.
Why EV is costly?
Because these batteries use lithium-ion technology (comprising rare earth materials), the cost of manufacturing increases. For larger vehicles, this is even costlier. So, the battery is the simple reason why electric cars are expensive.
What is the full form of EV battery?
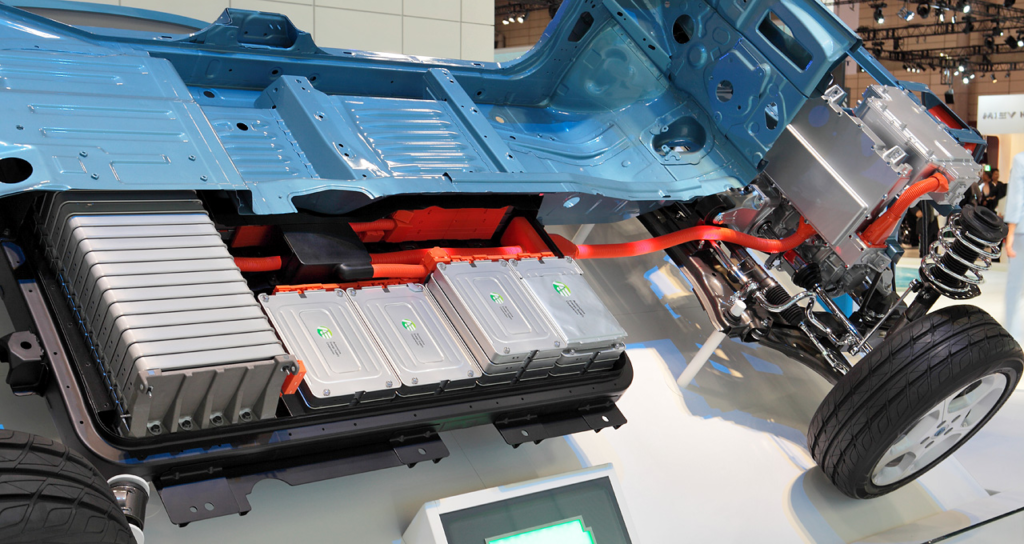

An electric vehicle battery (EVB, also known as a traction battery) is a rechargeable battery used to power the electric motors of a battery electric vehicle (BEV) or hybrid electric vehicle (HEV).
What are the three types of EV charging?
Another key thing to know from the outset: There are three categories or types of charging: Trickle Charge, AC Charge and DC Charge.
Why do we need EV charging?
Electric vehicles use electricity to charge their batteries instead of using fossil fuels like petrol or diesel. Electric vehicles are more efficient, and that combined with the electricity cost means that charging an electric vehicle is cheaper than filling petrol or diesel for your travel requirements.
- Connectivity of EV charging stations. …
- Balance your energy flow. …https://www.seai.ie/technologies/electric-vehicles/what-is-an-electric-vehicle/how-electric-vehicles-work/#:~:text=An%20electric%20vehicle%20uses%20a,improved%20hugely%20in%20recent%20years.
- Leverage your EV battery capacity. …
- Optimize sustainable energy usage. …
- Save on electricity costs.
What is the basic concept of EV?
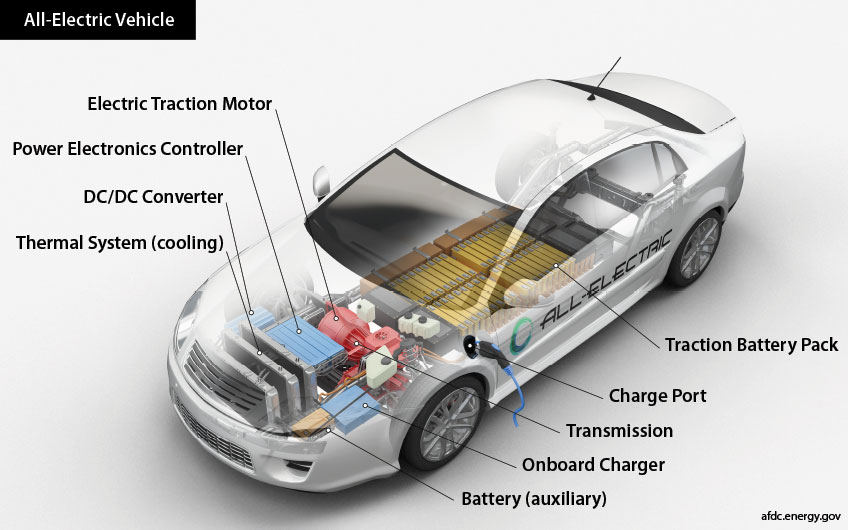
An all-electric vehicle (EV) uses a battery to store the electrical energy that powers the motor. EV batteries are charged by plugging the vehicle into an electric power source.
How is EV charging carried out?
Through a connector or plug, an EV charger delivers electric current to the electric vehicle from the grid. To power its electric motor, an electric vehicle stores that electricity in a large battery pack.
An electric vehicle (EV) charger’s connector is connected via a charging cable to the electric vehicle’s inlet, which is comparable to a conventional vehicle’s gas tank.
Only direct current (DC) power is accepted by EV batteries.
What are the various charging levels for electric vehicles?
There are three main types of charging for electric vehicles: Levels 1, 2, and 3 are typically referred to as DC fast charging or rapid charging.
A standard 120-volt wall plug, which can be found in most homes and garages in the United States, can be used to charge the Level 1 device. Level 1 charging is typically reserved for home charging at night because it is extremely slow. Level 1 charging can take more than 24 hours to fully charge an electric vehicle battery.
Level 2 chargers are typically found in homes and public charging stations and operate on 240 volts. A Level 2 charger is up to 15 times faster than a Level 1 charger! An electric clothes dryer-compatible 208- or 240-volt outlet is required for Level 2 EV charging stations. A dedicated circuit must be installed by an electrician because the majority of homes lack such an additional outlet in the garage or driveway.
The quickest way to charge an electric vehicle is with a DC fast charger or rapid charger, which uses more than 480 volts.
Level 1 and Level 2 chargers supply an electric vehicle with alternating current (AC), which is transformed into direct current (DC) by the vehicle’s battery. DC power can only be delivered to an EV battery. A DC rapid charging station, on the other hand, delivers DC directly to the electric vehicle without converting the electrical current. Due to the AC/DC conversion process, Level 1 and Level 2 chargers recharge electric vehicles much more slowly.
Level 3 charging, also known as DC fast charging, comes in three flavors: CHAdeMO (pronounced “CHArge de MOve”), the Tesla Supercharger, and the Combined Charging System (CCS). Cars equipped with CHAdeMO have a separate port for AC charging, whereas CCS permits AC/DC charging through the same port.
A DC fast charger is not suitable for all electric vehicles. DC fast chargers are only used in commercial settings and can’t be installed in homes for a number of reasons. First, homes don’t have enough electrical capacity for a DC rapid charger, electric vehicle drivers don’t need that fast of a charge for overnight home charging, and installing a DC fast charger is much more expensive than installing a Level 2 charger because of the improvements that need to be made to the electrical infrastructure.
A DC fast charging station, on the other hand, may be the best EV charging option for a business in terms of commercial applications. DC rapid chargers, for instance, are ideal for highway public charging stations and fleet charging.
Here, you can learn more about fleet charging.
What is the speed of Tesla Superchargers?
Over 25,000 Tesla Superchargers can be found worldwide. Tesla claims to have the world’s largest fast-charging network.
A Tesla battery can be charged in about 30 minutes at a Tesla Supercharger. Home installations of Tesla Superchargers are not permitted. A Supercharger is the only way for a Tesla EV driver to charge in public places like shopping malls, retail establishments, or along roadways.
What is the advantage of electric vehicle charging?

Electric vehicles use electricity to charge their batteries instead of using fossil fuels like petrol or diesel. Electric vehicles are more efficient, and that combined with the electricity cost means that charging an electric vehicle is cheaper than filling petrol or diesel for your travel requirements.
What are the disadvantages for the charging stations for electric cars?
Potential damage to your battery: While public charging stations are usually safe for your battery, constantly using Level 3 fast-charging stations can cause your EV’s battery to degrade faster than using Level 1 or Level 2 chargers for the majority of your charges.
What are the disadvantages of electric vehicles charging?
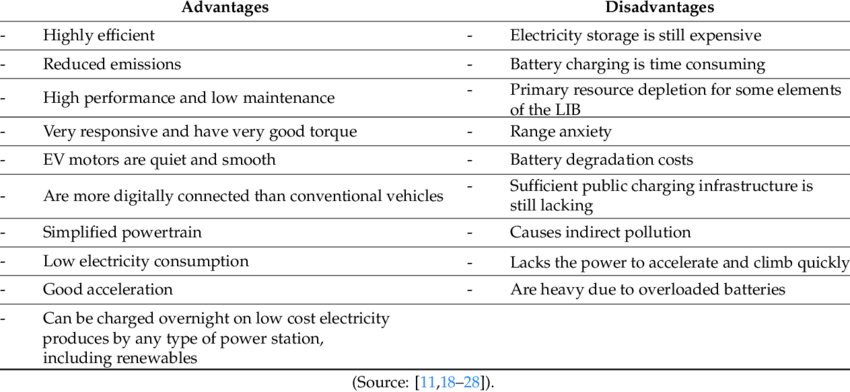
Disadvantages of Electric Vehicles
- Higher Purchase Cost. Compared to regular automobiles, electric vehicles are highly pricey. …
- Low Speed and Range. …
- Low Price on Selling. …
- The Inconvenience of Service Station. …
- Low Energy. …
- Battery Expenses. …
- Slow Charging. …
- Expensive Recharging Options.
Reference:
- https://www.seai.ie/technologies/electric-vehicles/what-is-an-electric-vehicle
- https://www.bonney.com


















