Introduction:
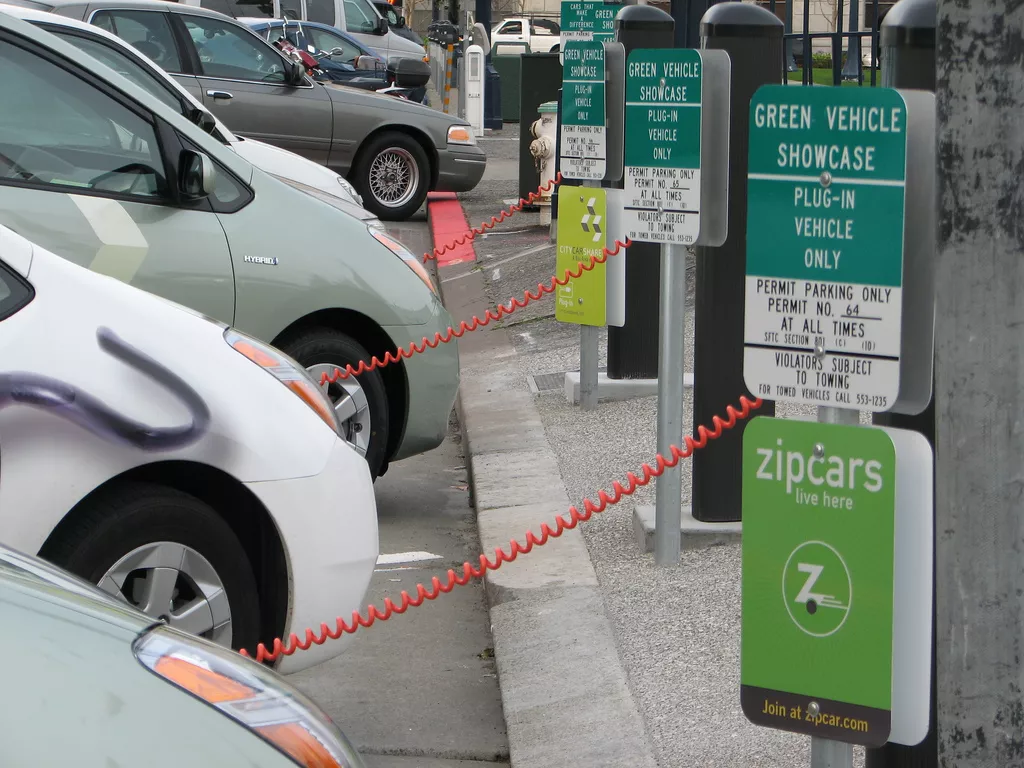
The automobile industry is rapidly evolving, and with the advent of electric cars, there is a growing interest in plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs). PHEVs are a type of hybrid car that combines the benefits of both electric and gas-powered engines, providing an efficient and environmentally friendly option for drivers. In this blog post, we will discuss what a PHEV is, how it works, its advantages and disadvantages, and its future in the automobile industry.
What is a Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)?
A PHEV is a type of hybrid car that combines a gas-powered engine with an electric motor and battery. PHEVs have larger batteries than traditional hybrid cars, which can be charged by plugging them into an electrical outlet. This means that PHEVs can run solely on electric power for a certain distance before the gas-powered engine takes over.
How Does a PHEV Work?
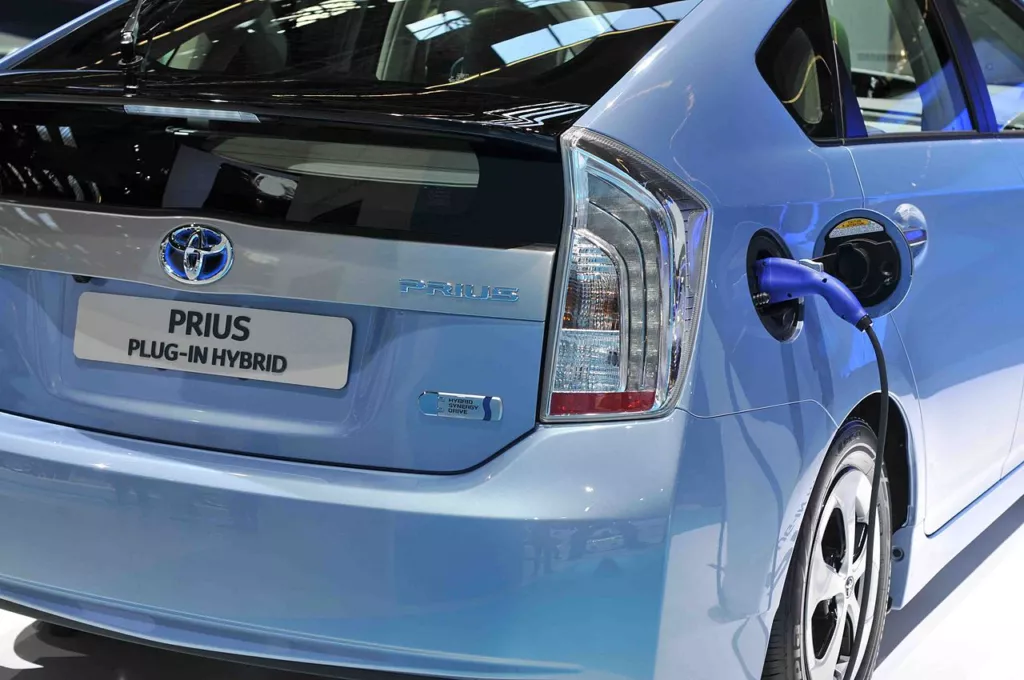

PHEVs have two power sources – an electric motor and a gas-powered engine. The electric motor is powered by a battery that can be charged by plugging the car into an electrical outlet. When the battery is fully charged, the PHEV can run solely on electric power for a certain distance.
Once the battery is depleted, the gas-powered engine takes over, providing power to the electric motor and recharging the battery. The engine can also provide additional power when the car needs to accelerate quickly or climb a steep hill.
Advantages of a PHEV:
- Environmentally Friendly: PHEVs produce less emissions than traditional gas-powered cars, making them more environmentally friendly.
- Fuel Efficiency: PHEVs use less fuel than traditional gas-powered cars, reducing the cost of fuel and saving money for drivers.
- Increased Range: PHEVs have a longer range than pure electric cars, as they can switch to the gas-powered engine when the battery is depleted.
- Tax Credits: PHEVs are eligible for tax credits from the government, making them more affordable for buyers.
Disadvantages of a PHEV:
- Higher Cost: PHEVs are more expensive than traditional gas-powered cars, making them less accessible to some buyers.
- Limited Electric Range: The electric range of PHEVs is limited, and once the battery is depleted, the car must rely on the gas-powered engine.
- Limited Charging Infrastructure: There is a limited availability of charging infrastructure for PHEVs, making it difficult to charge them in some areas.
The Future of PHEVs:
PHEVs are becoming more popular as consumers become more environmentally conscious and seek more fuel-efficient cars. The technology behind PHEVs is also improving, with larger batteries and longer electric ranges. It is likely that PHEVs will become even more popular in the coming years as the automobile industry continues to evolve.
Cost comparison between a PHEV-10 and a PHEV-40[152][154]
(prices for 2010)
| Plug-in type by EV range | Similar production model | Type of drivetrain | Manufacturer additional cost compared to conventional non-hybrid mid-size | Estimated cost of battery pack | Cost of electric system upgrade at home | Expected gasoline savings compared to a HEV | Annual gasoline savings compared to a HEV(2 | |
| PHEV-10 16 km | Prius Plug-in(1) | Parallel | US$6,300 | US$3,300 | More than US$1,000 | 20% | 260 L (70 US gal; 58 imp gal) | |
| PHEV-40 64 km | Chevy Volt | Series | US$18,100 | US$14,000 | More than US$1,000 | 55% | 760 L (200 US gal; 170 imp gal) | |
What do you mean by plug in hybrid electric vehicle?
Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) use batteries to power an electric motor, as well as another fuel, such as gasoline or diesel, to power an internal combustion engine or other propulsion source. PHEVs can charge their batteries through charging equipment and regenerative braking.
Conclusion:

PHEVs are a type of hybrid car that combines the benefits of electric and gas-powered engines. They are more environmentally friendly and fuel-efficient than traditional gas-powered cars, but they are also more expensive and have a limited electric range. The future of PHEVs looks promising, with improvements in battery technology and a growing interest in environmentally friendly cars. As the automobile industry continues to evolve, PHEVs will likely become more accessible and popular among consumers.
FAQs:
Q1. What is a PHEV?
Ans. A PHEV is a type of hybrid car that combines a gas-powered engine with an electric motor and battery. PHEVs have larger batteries than traditional hybrid cars, which can be charged by plugging them into an electrical outlet.
Q2. How does a PHEV work?
Ans. PHEVs have two power sources – an electric motor and a gas-powered engine. The electric motor is powered by a battery that can be charged by plugging the car into an electrical outlet. Once the battery is depleted, the gas-powered engine takes over, providing power to the electric motor and recharging the battery.
Q3. What are the advantages of a PHEV?
Ans. Some advantages of a PHEV include being more environmentally friendly, having increased fuel efficiency, having a longer range than pure electric cars, and being eligible for tax credits.
Q4. What are the disadvantages of a PHEV?
Ans. Some disadvantages of a PHEV include being more expensive than traditional gas-powered cars, having a limited electric range, and limited charging infrastructure.
Q5. How much does a PHEV cost?
Ans. The cost of a PHEV varies depending on the make and model, but they are generally more expensive than traditional gas-powered cars.
Q6. How far can a PHEV go on electric power?
Ans. The electric range of PHEVs varies depending on the make and model, but it is typically around 20-50 miles before the gas-powered engine takes over.
Q7. How do I charge a PHEV?
Ans. PHEVs can be charged by plugging them into a standard electrical outlet or a specialized charging station.
Q8. How long does it take to charge a PHEV?
Ans. The time it takes to charge a PHEV depends on the battery size and the charging method. It can take anywhere from a few hours to overnight to fully charge a PHEV.
Q9. Are PHEVs eligible for government incentives?
Ans. Yes, PHEVs are eligible for tax credits from the government, making them more affordable for buyers.
Q10. Are PHEVs better for the environment than traditional gas-powered cars?
Ans. Yes, PHEVs produce less emissions than traditional gas-powered cars, making them more environmentally friendly.























