Introduction:
Fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) are a type of electric vehicle that use hydrogen as their fuel source. FCEVs offer a number of advantages over traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, including zero-emissions driving and longer driving ranges. In this blog post, we will explore the definitions, working principles, advantages, and disadvantages of fuel cell electric vehicles.
What is a Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle?
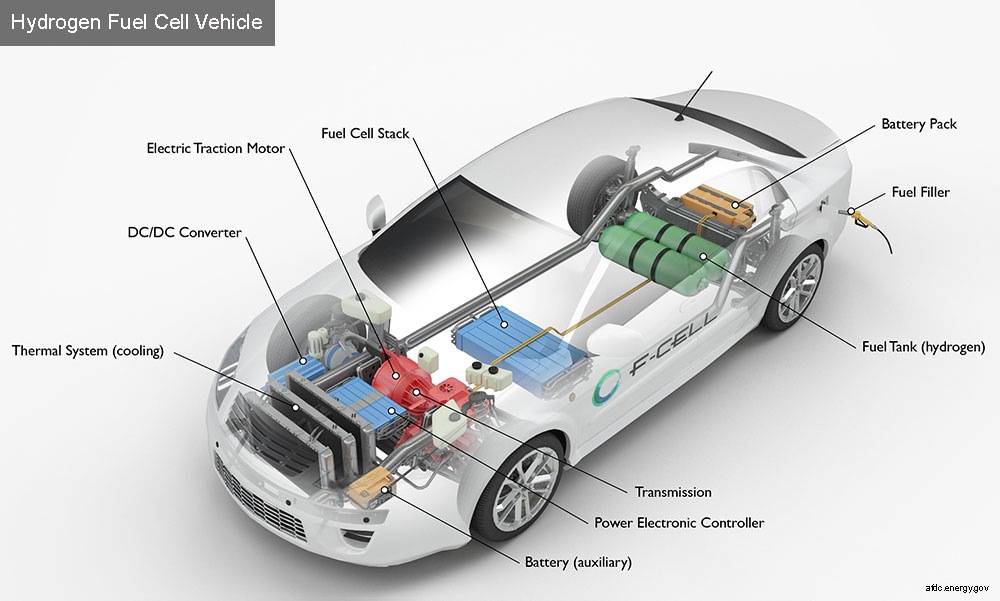
A fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV) is a type of electric vehicle that uses a fuel cell to convert hydrogen into electricity to power an electric motor. FCEVs do not produce any emissions, as their only byproduct is water.
How does a Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle Work?

FCEVs work by using a fuel cell to convert hydrogen into electricity. The fuel cell contains an anode, a cathode, and an electrolyte. Hydrogen gas is fed into the anode, while oxygen is fed into the cathode. The two gases combine in the fuel cell, producing electricity, water, and heat. The electricity is used to power the vehicle’s electric motor, while the water and heat are released as byproducts.
Advantages of Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles:
- Zero Emissions – FCEVs produce zero emissions, making them an environmentally friendly alternative to ICE vehicles.
- Longer Driving Range – FCEVs have a longer driving range than battery electric vehicles (BEVs), as they can be refueled much faster and have a higher energy density.
- Fast Refueling – Refueling an FCEV takes only a few minutes, compared to the hours it takes to recharge a BEV’s battery.
- Quiet Operation – FCEVs operate quietly, making them a good option for urban environments.
Disadvantages of Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles:
- Limited Availability – FCEVs are currently less widely available than traditional ICE vehicles or BEVs.
- High Cost – FCEVs are currently more expensive than traditional ICE vehicles or BEVs.
- Limited Refueling Infrastructure – There are currently limited refueling stations for FCEVs, making it difficult to refuel in some areas.
Conclusion:

Fuel cell electric vehicles offer a number of advantages over traditional ICE vehicles and BEVs, including zero-emissions driving and longer driving ranges. However, they also have their disadvantages, including limited availability, high cost, and limited refueling infrastructure. As technology continues to develop, it is possible that FCEVs will become more widely available and affordable, making them a viable alternative to traditional ICE vehicles and BEVs.
FAQs:
Q1. What is a fuel cell electric vehicle?

Ans. A fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV) is a type of electric vehicle that uses a fuel cell to convert hydrogen into electricity to power an electric motor.
Q2. How does a fuel cell work in an FCEV?
Ans. The fuel cell contains an anode, a cathode, and an electrolyte. Hydrogen gas is fed into the anode, while oxygen is fed into the cathode. The two gases combine in the fuel cell, producing electricity, water, and heat.
Q3. What is the range of an FCEV?
Ans. FCEVs have a longer driving range than battery electric vehicles (BEVs), as they can be refueled much faster and have a higher energy density.
Q4. How long does it take to refuel an FCEV?
Ans. Refueling an FCEV takes only a few minutes, compared to the hours it takes to recharge a BEV’s battery.
Q5. What is the availability of FCEVs?
Ans. FCEVs are currently less widely available than traditional ICE vehicles or BEVs, but their availability is increasing.
Q6. Are FCEVs more expensive than traditional ICE vehicles?
Ans. FCEVs are currently more expensive than traditional ICE vehicles or BEVs.
Q7. Do FCEVs produce emissions?
Ans. FCEVs produce zero emissions, as their only byproduct is water.
Q8. Are FCEVs suitable for long-distance driving?
Ans. Yes, FCEVs are suitable for long-distance driving, as they have a longer driving range than BEVs.
Q9. Is there a refueling infrastructure for FCEVs?
Ans. There are currently limited refueling stations for FCEVs, making it difficult to refuel in some areas.
Q10. Can FCEVs be serviced at traditional auto repair shops?
Ans. FCEVs require specialized knowledge and equipment, so they should be serviced at certified FCEV repair shops.
Q11. Which fuel cell is used in electric vehicles?
Fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) are powered by hydrogen. They are more efficient than conventional internal combustion engine vehicles and produce no harmful tailpipe emissions—they only emit water vapor and warm air. FCEVs and the hydrogen infrastructure to fuel them are in the early stages of implementation.