Introduction:
The internal combustion engine (ICE) has revolutionized the way we live, work and travel. It has been the heart of automobiles, boats, aircraft, and many other machines that have shaped the modern world. In this blog post, we will explore the working of the internal combustion engine, its history, types, and the impact it has had on our lives.
What is an Internal Combustion Engine?
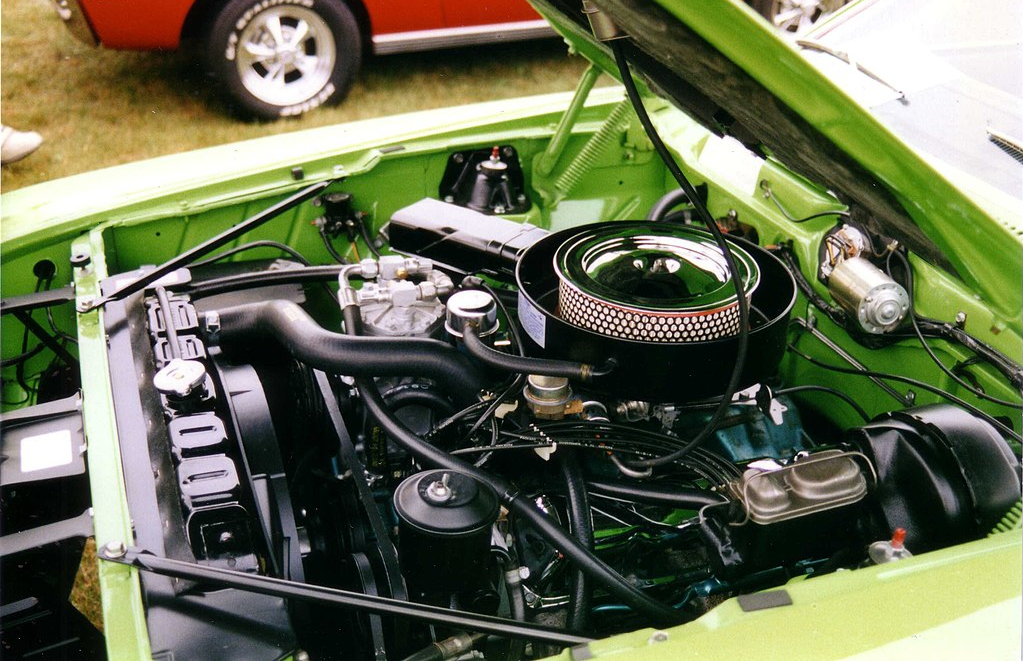
An ICE is a heat engine that converts the chemical energy stored in fuel into mechanical energy. It works by burning fuel and air inside the engine to produce a high-pressure mixture of hot gases. This mixture then expands rapidly, pushing a piston or a turbine, which in turn produces mechanical energy. This mechanical energy can be used to power machines or vehicles.
A Brief History of the Internal Combustion Engine:
The first practical internal combustion engine was invented by French engineer Etienne Lenoir in 1860. It was a two-stroke engine that used coal gas as fuel. However, it was not until the late 19th century that the internal combustion engine started to become widely used. In 1876, German engineer Nikolaus Otto invented the four-stroke engine, which is still widely used in automobiles today. Since then, the internal combustion engine has undergone significant improvements and has become an essential part of modern life.
How Does an Internal Combustion Engine Work?
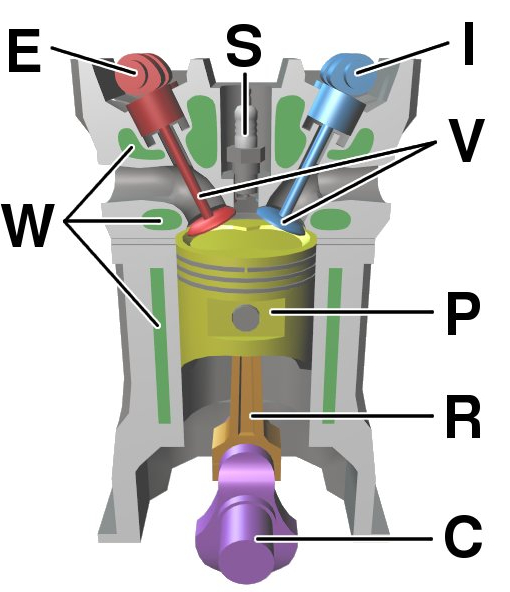
An ICE works by following four basic steps: intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust. During the intake stroke, the engine takes in air and fuel through an intake valve. Then, during the compression stroke, the piston compresses the air-fuel mixture, increasing its pressure and temperature. When the piston reaches the top of the stroke, the spark plug ignites the mixture, causing it to burn rapidly, and creating high-pressure gases that expand, pushing the piston back down the cylinder. This is the power stroke. Finally, during the exhaust stroke, the piston pushes the remaining gases out of the cylinder through an exhaust valve.
Types of Internal Combustion Engines:
There are two main types of internal combustion engines: gasoline engines and diesel engines. Gasoline engines use a spark plug to ignite the air-fuel mixture, while diesel engines rely on the heat generated by compressing the air in the cylinder. Gasoline engines are generally used in cars, while diesel engines are more common in trucks, buses, and large vehicles. Another type of internal combustion engine is the Wankel engine, which uses a rotary design instead of the traditional piston-cylinder design.
The Impact of Internal Combustion Engines on Our Lives:
The internal combustion engine has had a significant impact on our lives, allowing us to travel faster and farther than ever before. It has enabled the development of automobiles, airplanes, boats, and many other machines that have shaped the modern world. However, the widespread use of internal combustion engines has also had negative consequences, such as air pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and dependence on fossil fuels. As a result, there is growing interest in alternative sources of energy, such as electric vehicles and renewable energy sources.
Conclusion:

The internal combustion engine has been one of the most significant inventions of the modern era. It has enabled us to travel faster and farther than ever before and has been the driving force behind the development of modern transportation. However, it has also had negative consequences, such as air pollution and dependence on fossil fuels. As we look to the future, there is a growing need to find alternative sources of energy and to develop more sustainable transportation systems.
FAQs:
Q1. What is an ICE?
Ans. An ICE is a heat engine that converts the chemical energy stored in fuel into mechanical energy by burning fuel and air inside the engine.
Q2. How does an ICE work?
Ans. An ICE works by following four basic steps: intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust. During the intake stroke, the engine takes in air and fuel through an intake valve. Then, during the compression stroke, the piston compresses the air-fuel mixture, increasing its pressure and temperature. When the piston reaches the top of the stroke, the spark plug ignites the mixture, causing it to burn rapidly, and creating high-pressure gases that expand, pushing the piston back down the cylinder. This is the power stroke. Finally, during the exhaust stroke, the piston pushes the remaining gases out of the cylinder through an exhaust valve.
Q3. What fuels can be used in an internal combustion engine?
Ans. Gasoline and diesel are the most common fuels used in ICE. However, alternative fuels like biofuels, natural gas, and hydrogen can also be used.
Q4. What is the difference between a gasoline engine and a diesel engine?
Ans. Gasoline engines use a spark plug to ignite the air-fuel mixture, while diesel engines rely on the heat generated by compressing the air in the cylinder. Gasoline engines are generally used in cars, while diesel engines are more common in trucks, buses, and large vehicles.
Q5. What is the history of the internal combustion engine?
Ans. The first practical internal combustion engine was invented by French engineer Etienne Lenoir in 1860. It was a two-stroke engine that used coal gas as fuel. The four-stroke engine was invented by German engineer Nikolaus Otto in 1876, which is still widely used in automobiles today.
Q6. What is the most common type of internal combustion engine?
Ans. The most common type of internal combustion engine is the gasoline engine, which is used in most automobiles.
Q7. What is the Wankel engine?
Ans. The Wankel engine is a type of ICE that uses a rotary design instead of the traditional piston-cylinder design.
Q8. What are the advantages of internal combustion engines?
Ans. Internal combustion engines are reliable, powerful, and can be used in a wide range of applications. They have been used to power automobiles, boats, aircraft, and many other machines that have shaped the modern world.
Q9. What are the disadvantages of internal combustion engines?
Ans. Internal combustion engines are a significant source of air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. They also rely on fossil fuels, which are a finite resource and have environmental impacts.
Q10. What is the future of internal combustion engines?
Ans. The future of internal combustion engines is uncertain. While they will likely continue to be used in some applications, there is a growing need to find alternative sources of energy and to develop more sustainable transportation systems. This has led to a growing interest in electric vehicles and renewable energy sources.























