Introduction:
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on inverters, the unsung heroes of electricity conversion! In this blog post, we will delve into the fascinating world of inverters, exploring their functionality, types, applications, and benefits. Whether you’re a homeowner, a renewable energy enthusiast, or simply curious about this innovative technology, you’ve come to the right place. So, let’s embark on this electrifying journey together!
What is an Inverter?
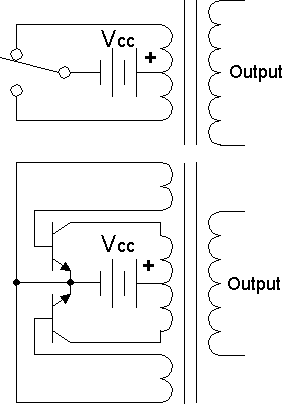
An inverter is an electronic device that converts direct current (DC) electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity. It plays a vital role in our daily lives by enabling the use of AC-powered appliances and devices, such as televisions, refrigerators, air conditioners, and more. Inverters are the backbone of various applications, from residential setups to large-scale industrial systems.
How Does an Inverter Work?
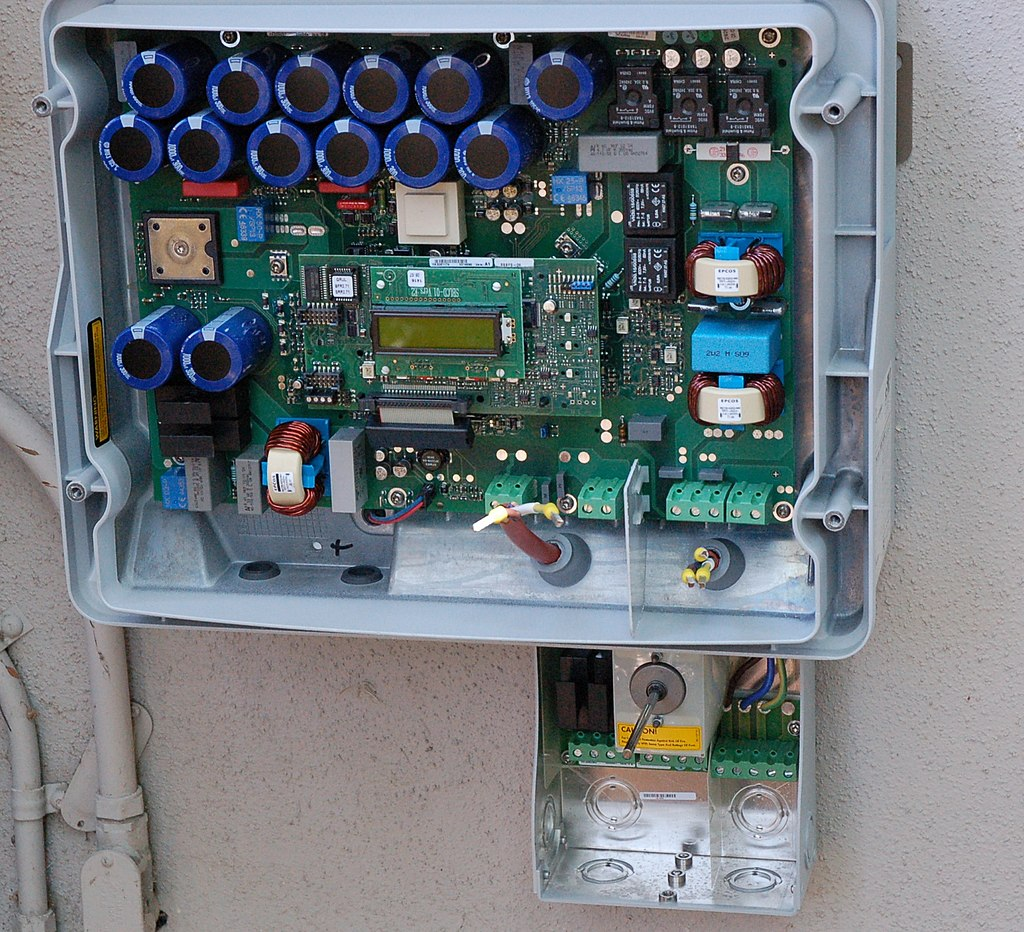

Inverters utilize advanced circuitry to transform the DC electricity from sources like batteries or solar panels into AC electricity compatible with standard power grids or home appliances. Through a process called inversion, inverters convert the steady flow of DC electricity into the oscillating form of AC electricity, allowing for seamless utilization of electrical energy.
Types of Inverters:
Inverters come in various types to cater to different needs and applications.
Standalone Inverters:
Standalone inverters, also known as off-grid inverters, are designed for systems that are not connected to the utility grid. They are commonly used in remote areas or for emergency backup power, providing autonomy and independence from the grid.
Grid-Tied Inverters:
Grid-tied inverters, as the name suggests, are designed to work in conjunction with the utility grid. They convert DC electricity from renewable energy sources, such as solar panels or wind turbines, into AC electricity that can be fed back into the grid. These inverters allow for net metering, where excess electricity produced can be sold back to the utility company.
Battery-Based Inverters:
Battery-based inverters, also known as inverter chargers, are designed to work with energy storage systems. They not only convert DC electricity to AC for immediate use but also facilitate charging and discharging of batteries. These inverters are commonly used in off-grid or hybrid setups, providing a reliable backup power source.
Hybrid Inverters:
Hybrid inverters combine the functionalities of grid-tied and battery-based inverters. They can operate with or without a grid connection, making them versatile for both on-grid and off-grid applications. Hybrid inverters are ideal for homeowners seeking the benefits of renewable energy and backup power.
Applications of Inverters:
Inverters find applications across diverse sectors and industries.
Residential Applications:
In residential settings, inverters are used to power everyday appliances, lighting, and entertainment systems. With the rise of solar power systems, homeowners can generate their own electricity and use inverters to convert it into usable AC power.
Commercial Applications:
Many commercial establishments, such as offices, retail stores, and hotels, rely on inverters to power their operations. Inverters help to ensure uninterrupted power supply, reducing downtime and improving business efficiency.
Industrial Applications:
Industries heavily depend on inverters for machinery and equipment operation. Inverters enable precise control of motor speed, resulting in energy savings and enhanced productivity in sectors like manufacturing, food processing, and more.
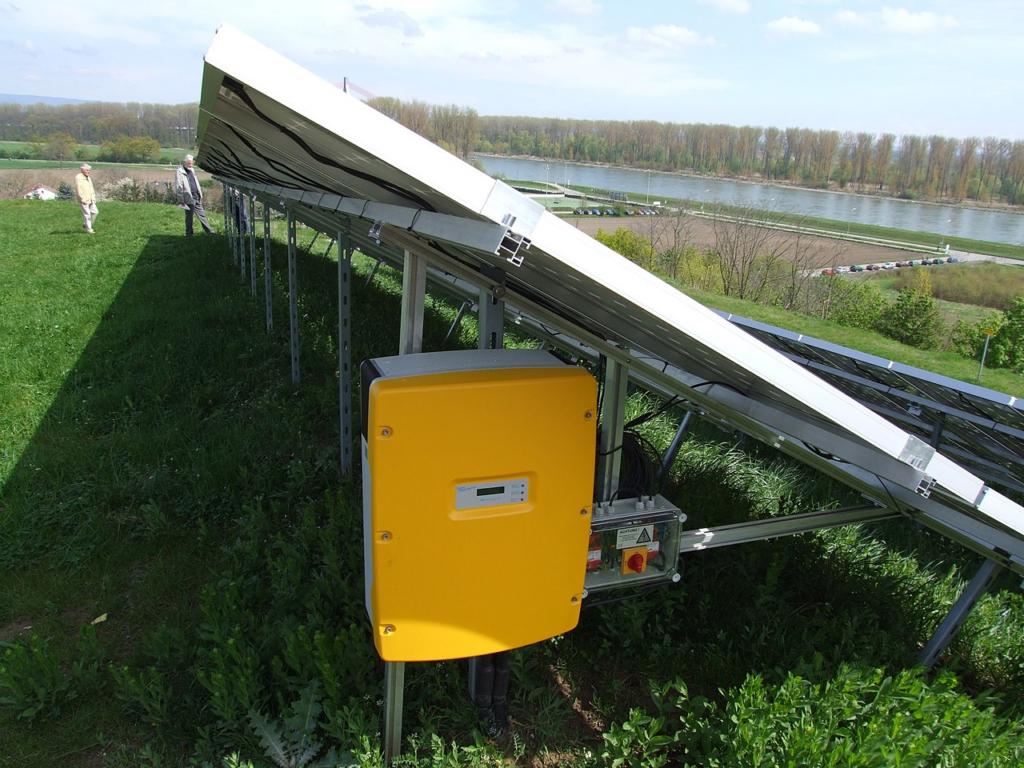
Renewable Energy Applications:
Inverters play a crucial role in renewable energy systems, such as solar and wind power. They convert the DC electricity generated by solar panels or wind turbines into AC electricity that can be used directly or fed into the grid.
Benefits of Using an Inverter:
Inverters offer a range of benefits that make them an invaluable addition to various applications.
Energy Efficiency:
By converting DC electricity to AC, inverters enable the efficient use of electrical energy. They minimize energy losses and ensure optimal utilization, resulting in cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
Backup Power Supply:
Inverters equipped with battery storage provide a reliable backup power supply during grid outages or emergencies. This feature is particularly beneficial for homeowners, businesses, and critical facilities that cannot afford disruptions in power supply.
Reduced Carbon Footprint:
Incorporating inverters in renewable energy systems promotes a greener and more sustainable future. By harnessing solar or wind power and converting it into usable AC electricity, inverters contribute to reducing reliance on fossil fuels, lowering carbon emissions, and mitigating environmental impact.
Cost Savings:
For homeowners and businesses, utilizing inverters in conjunction with renewable energy sources can lead to significant cost savings on electricity bills. By generating their own power and potentially selling excess energy back to the grid, users can offset their energy costs and even generate additional income.
Choosing the Right Inverter:
Selecting the appropriate inverter for your specific needs is crucial for optimal performance and efficiency.
Power Requirements:
Consider your power requirements and the load you intend to connect to the inverter. Assess the wattage and voltage requirements of your appliances to ensure compatibility and sufficient power capacity.
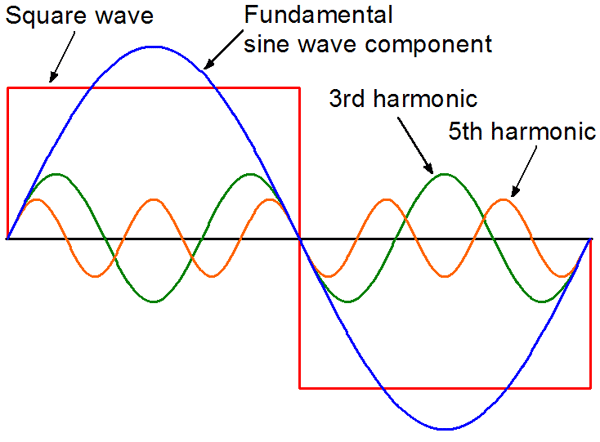
Waveform Type:
Inverters produce either a pure sine wave or a modified sine wave. Pure sine wave inverters deliver a clean and stable waveform, suitable for sensitive electronics and appliances. Modified sine wave inverters are more affordable but may not be compatible with certain devices.
Efficiency Ratings:
Pay attention to the efficiency ratings of inverters. Higher efficiency means less energy loss during conversion, resulting in greater overall energy savings.
Budget Considerations:
Set a budget range for your inverter purchase while considering your requirements. Strike a balance between quality, features, and affordability to make an informed decision.
Installation and Maintenance Tips:
Proper installation and regular maintenance are essential for the smooth operation and longevity of inverters.
Professional Installation:
Engage a professional electrician or an experienced installer to ensure correct installation and safe electrical connections. Improper installation can compromise performance and even pose safety risks.
Regular Maintenance:
Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for maintenance, including cleaning, inspection, and testing. Regularly check the inverter’s components, connections, and ventilation to identify and address any issues promptly.
Safety Precautions:
Always adhere to safety precautions when working with electricity. Turn off the inverter and disconnect it from the power source before performing any maintenance or troubleshooting tasks. Take necessary precautions to prevent electrical shocks and accidents.
Conclusion:

Inverters are the unsung heroes that enable the seamless conversion of electricity, powering our everyday lives and driving the growth of renewable energy. Whether you’re seeking energy independence, backup power, or a sustainable future, inverters offer a versatile solution. By understanding the types, applications, and benefits of inverters, you can make informed decisions and harness their full potential. Embrace the power of inverters and unlock a world of efficient and sustainable energy conversion!























