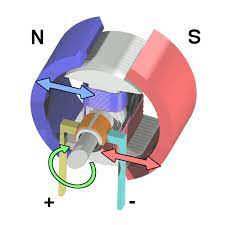
Introduction:
Motor is an essential part of modern life, powering everything from household appliances to heavy machinery. In this blog post, we will explore what a motor is, how it works, and the different types of motors available. We will also discuss the importance of motor in our daily lives and the future of motor technology.
What is a Motor?
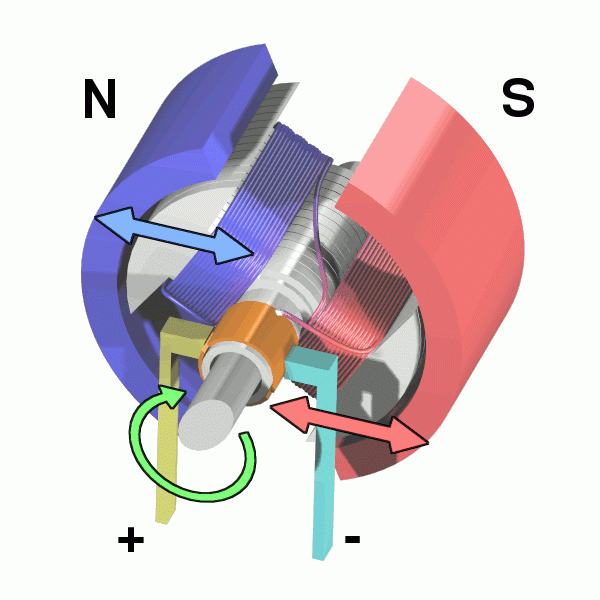
A motor is a machine that converts electrical or other types of energy into mechanical energy. It is a device that produces rotational motion, which can be used to power machines and equipment. Motors are used in a wide range of applications, from small household appliances to large industrial equipment.
How does a Motor Work?
Motors work by using the interaction between magnetic fields to produce motion. A motor consists of a rotating component, called the rotor, and a stationary component, called the stator. The stator contains a series of coils that are energized by an electrical current, producing a magnetic field. The rotor contains a series of permanent magnets that interact with the magnetic field produced by the stator, causing the rotor to rotate.
Types of Motor:
There are many different types of motor, each with its unique characteristics and applications. Some of the most common types of motors include:
- DC Motor: These motors use direct current (DC) to produce rotational motion. They are commonly used in small household appliances and toys.
- AC Motor: These motors use alternating current (AC) to produce rotational motion. They are commonly used in large industrial equipment and appliances.
- Brushless Motor: These motors are similar to DC motor but do not use brushes to transfer power between the stator and rotor. They are commonly used in drones, electric vehicles, and other high-performance applications.
- Stepper Motor: These motors use electromagnetic fields to produce precise, incremental movements. They are commonly used in printers, scanners, and other devices that require precise control.
- Electric motor: An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor’s magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate force in the form of torque applied on the motor’s shaft. An electric generator is mechanically identical to an electric motor, but operates with a reversed flow of power, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Importance of Motors in Our Daily Lives:
Motor is an essential part of modern life, powering a wide range of devices and machines that we use every day. They are used in everything from kitchen appliances to industrial equipment and are essential for transportation, communication, and entertainment.
The Future of Motor Technology:
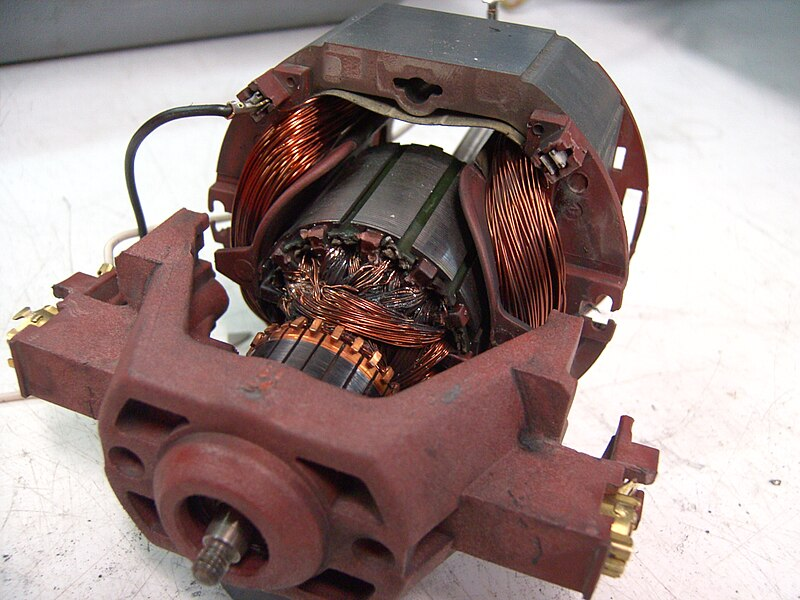
The future of motor technology is bright, with new advances being made every day. There is a growing interest in electric motors, which are more efficient and environmentally friendly than traditional combustion engines. Additionally, advances in robotics and automation are leading to new applications for motors in fields like manufacturing and healthcare.
Conclusion:

In conclusion, motor is an essential part of modern life, powering everything from household appliances to heavy machinery. They work by using magnetic fields to produce rotational motion and come in many different types, each with its unique characteristics and applications. As we look to the future, there is a growing interest in electric motors and automation, which will undoubtedly lead to new and exciting applications for this important technology.
FAQs:
Q1. What is a motor?
Ans. A motor is a machine that converts electrical or other types of energy into mechanical energy to produce rotational motion.
Q2. How does a motor work?
Ans. Motors work by using the interaction between magnetic fields to produce motion. A motor consists of a rotating component, called the rotor, and a stationary component, called the stator.
Q3. What are the different types of motors?
Ans. There are many different types of motors, including DC motor, AC motor, brushless motor, and stepper motor.
Q4. What is a DC motor?
Ans. A DC motor uses direct current (DC) to produce rotational motion. They are commonly used in small household appliances and toys.
Q5. What is an AC motor?
Ans. An AC motor uses alternating current (AC) to produce rotational motion. They are commonly used in large industrial equipment and appliances.
Q6. What is a brushless motor?
Ans. A brushless motor is similar to a DC motor but does not use brushes to transfer power between the stator and rotor. They are commonly used in drones, electric vehicles, and other high-performance applications.
Q7. What is a stepper motor?
Ans. A stepper motor uses electromagnetic fields to produce precise, incremental movements. They are commonly used in printers, scanners, and other devices that require precise control.
Q8. How important are motors in our daily lives?
Ans. Motors are essential in our daily lives, powering a wide range of devices and machines that we use every day. They are essential for transportation, communication, and entertainment.
Q9. What is the future of motor technology?
Ans. The future of motor technology is bright, with new advances being made every day. There is a growing interest in electric motors, which are more efficient and environmentally friendly than traditional combustion engines. Additionally, advances in robotics and automation are leading to new applications for motors in fields like manufacturing and healthcare.
Q10. What are some of the benefits of electric motors over traditional combustion engines?
Ans. Electric motors are more efficient, produce less pollution, and require less maintenance than traditional combustion engines. They are also quieter and can provide more precise control.