A Field Effect Transistor (FET) is a three-terminal active semiconductor device in which an electric field brought about by the input voltage controls the output current. Because, in contrast to bipolar transistors, FETs only employ electrons or holes as charge carriers, they are also referred to as unipolar transistors. The Field Effect Transistor is a “Voltage-operated device” because the voltage applied to its input terminal (the Gate) controls the current flowing from the source to the drain.
Due to their small size and low power consumption, FETs are frequently used in Integrated Circuits (ICs). Aside from that, FETs are additionally utilized in high power exchanging applications, as voltage-variable resistors (VVRs) in functional enhancers (Operation Amps), and tone controls, and so forth., for blender procedure on FM and Television inputs and in rationale circuits.
Field Effect Transistor (FET) – Psychical Overview
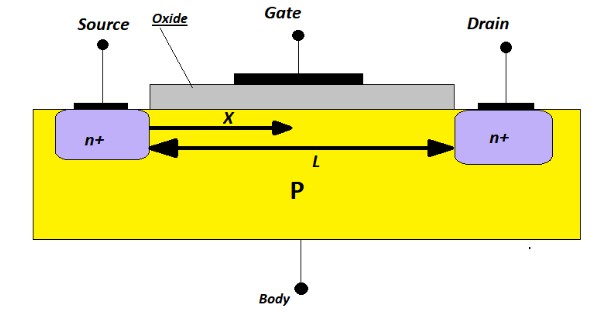
The Source, Drain, Gate, and Body terminals make up a FET.
Source: The terminal through which the majority of charge carriers enter the FET is called Source.
Drain: The majority of charge carriers exit the FET through the drain terminal.
Gate: Diffusion of a P-type semiconductor and an N-type semiconductor results in the formation of the gate terminal. This makes an intensely doped PN intersection locale that controls the progression of the transporter from source to deplete.
Body: The FET is constructed on this substrate. Because it is internally connected to the source pin, discrete applications can completely ignore its effects. However, since many transistors will share this pin, integrated circuits typically connect it to the most negative power supply in an NMOS circuit and the most positive power supply in a PMOS circuit. When the Body connection is involved, careful connections and design are essential for maintaining FET performance.
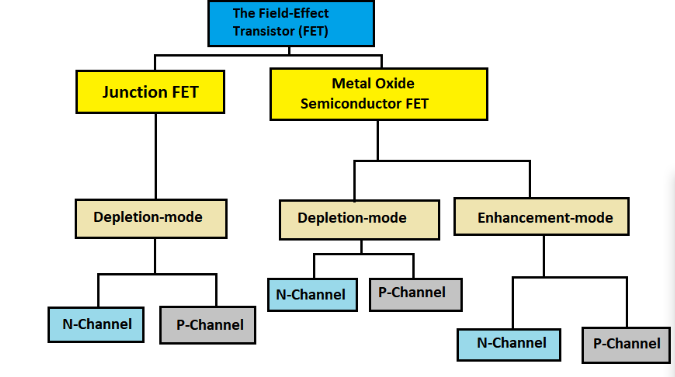
FET Classification
Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (MOSFET) transistors and Junction Field Effect transistors (JFET) are the two types of FET transistors.